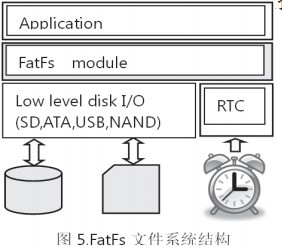
provide basic hardware access functions. . µC/FS is a high performance library that has been optimized for speed, versatility and memory footprint.
µC/FS is written in ANSI C and can be used on virtually any CPU. Some
features of µC/FS are:
· MS-DOS/MS-Windows compatible FAT12 and FAT16 support.
· Multiple device driver support. You can use different device drivers with µC/FS, which allows you to access different types of hardware with the file system at the same time. 【在該文件系統中可同時支持多個設備驅動】
· Multiple media support. A device driver does allow you to access different medias at the same time.
· OS support. µC/FS can easily be integrated into any OS. In that way you can make file operations in a multithreaded environment.
· ANSI C stdio.h like API for user applications. An application using standard C I/O library can easily be ported to use µC/FS.
· Very simple device driver structure. µC/FS device drivers need only very basic functions for reading and writing blocks. Therefore it is very simple to support your custom hardware.
· Generic device driver for SmartMedia cards, which can easily be used with any kind of card reader hardware.
· Generic device driver for MultitMedia & SD cards using SPI mode, which can be easily integrated.
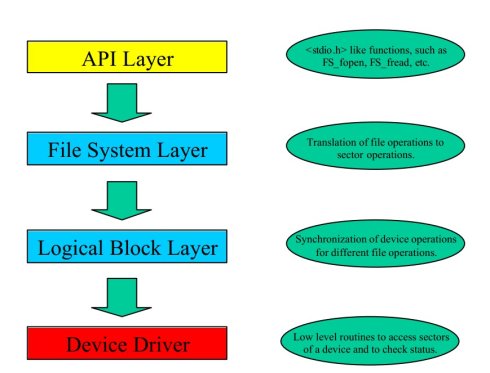
1:API層【類似于linux的VFS層】
The API layer is the interface between µC/FS and the user application. It does contain a library of ANSI C oriented file functions, such as FS_FOpen, FS_FWrite etc. The API layer does transfer these calls to the file system layer. Currently there is only a FAT file system layer available for µC/FS, but the API layer can deal with different file system layers at the same time. So it is possible to use FAT and any other file system at the same time with µC/FS.
API層是µC/FS 提供給用戶使用的接口層(fs_api.h),API層將各種調用傳輸到file system layer(文件系統層),目前對µC/FS(文件管理實現機制)來說 只有一個 FAT文件系統層被使用,API層可以處理不同的文件系統層,因此µC/FS可同時支持多種文件系統(API層類似于linux中的虛擬文件系統VFS,他的功能是提供給童用戶標準的系統調用接口,VFS層下面才是具體實際的文件系統層,有FAT、EXT2等等,這個根據硬件的情況(格式化時使用什么文件系統)來調用具體的文件系統)。
2:File System Layer 文件系統層【這層與linux是一樣的,是具體的管理文件所用的文件系統】
The file system layer translates file operations to logical block operations. After such a translation, the file system calls the logical block layer and specifies the corresponding device driver for a device.
文件系統層將文件操作轉換為邏輯塊操作,之后,具體的文件系統調用邏輯塊層函數并指定設備相應的驅動;【linux中,文件系統將各種系統調用轉換為各種IO請求(系統請求即是對底層相應的扇區、柱面、等操作),IO請求被放到對應設備的IO請求隊列中去,再由一個系統內核線程一直讀取請求隊列中的請求,沒有請求時就睡眠,拿到請求就通過設備驅動實現具體的操作】
uC_FS\FSL\fat\ 下面就是FAT文件系統的各個文件。
3:Logical Block Layer 邏輯塊層
the main purpose of the logical block layer is to synchronize accesses to a device driver and to have an easy interface for the file system layer. The logical block layer does call a device driver to make a block operation.
邏輯塊層的主要目的是同步訪問設備驅動與文件系統的簡易接口,邏輯塊層調用設備驅動來實現設備的塊操作。
4: Device Driver Layer 設備驅動層
Device drivers are low level routines that are used to access your hardware.
The structure of the device driver is simple to allow easy integration of your own
hardware.
設備驅動是一些訪問硬件的底層操作,µC/FS的設備驅動的架構很簡單,不像linux架構非常復雜。
4: uC/FS的使用
下面的流程是參考uC/FS用戶手冊上的例程來寫的,可以參考。
1:調用FS_Init()初始化文件系統,在使用uC/FS的任何功能函數之前須要首先調用該函數進行初始 化;
2:進入MainTask()
1:調用FS_IoCtl()【格式化:使硬件按指定的文件系統來管理文件】
This call is used to format your RAM disk in order to be able to write data to it. Formatting your RAM disk should not cause any problem.
2:調用應用程序中的函數_write_file()【非uc/fs的函數】
_write_file()中又依次調用: FS_FOpen(), FS_FWrite(),FS_FClose()
FS_FOpen():在這個例程中FS_FOpen()創建了一個叫default.txt的文件,如果創建成功,函數 將返回一個FS_FILE結構體的指針,如果出錯將返回0
FS_FWrite():文件創建成功之后,將一串字符串寫入該文件中,如果寫入時出錯,例程中調 用FS_FError()處理錯誤。
FS_FClose():關閉上面打開的文件,返回主任務中
【大致過程就是如上過程】
讀: FS_FOpen()->FS_FRead()->FS_FClose()
3:不使用uC/FS文件管理系統時調用FS_Exit().
5: uC/FS加入到工程中
1:Create a simple project without µC/FS
We recommend, that you create a small “hello world” program for your system. That project should already use your OS and there should be a way to display text on a screen or serial port.
2: Add your µC/FS configuration
In order to configure µC/FS for your system, you should create a new sub-directory in µC/FS’s config directory and copy the files fs_conf.h and fs_port.h from one of the other sub-directories to your directory. For the following chapters, we assume that you have created a directory FS\CONFIG\myconfig. Usually, the only file you have to modify is fs_conf.h. For an easy startup, we recommend, that you disable all drivers except the RAM disk driver. Please check out the chapter “Configuration of µC/FS” for detailed information about the configuration.
3: Add µC/FS generic source code
Add all source files in the following directories:
FS\API: µC/FS提供給用戶的接口函數
FS\FSL: 具體的文件系統層
FS\LBL: 邏輯塊層
FS\OS :
FS\DEVICE\RAM
and their sub-directories to your project.
4: Configure the search path[為開發環境添加所以代碼的路徑]
FS\API
FS\CONFIG\myconfig
FS\LBL
FS\OS
5: Add generic sample code
For a quick and easy test of your µC/FS integration, you should use the code
found in FS\sample\main.c.
6: uC/FS配置
1:fs_conf.h
This is the main configuration file for the file system. You define which drivers you want to use and, the configurations for these drivers.
【用戶手冊中列出了一個配置樣本】,包括下面的各個配置項目
1:OS support
You can specify whether you are using uC/OS-II, embOS, Windows or no OS support at all. Please set FS_OS_UCOS_II, FS_OS_EMBOS, FS_OS_WINDOWS to 1, respectively. For no OS support at all, set all of them to 0. If you need support for an additional OS, you will have to provide functions described in the chapter “OS integration”.
2:Time/Date support
If you want to be able to add date and times to your files, you will need to set
FS_OS_TIME_SUPPORT to 1.
3:File System Layer Support
µC/FS can support different file system at the same time. You can enable them by setting FS_USE_XXX_FSL, where XXX is the name of the file system layer. The current version of µC/FS only supports the FAT file system, so you will need to set FS_USE_FAT_FSL to 1.
4:Device Driver Support and configuration
I RAM Disk:
FS_USE_RAMDISK_DRIVER
to
1
Windows Driver: FS_USE_WINDRIVE_DRIVER to 1
Smart Media Card(SMCs):
FS_USE_SMC_DRIVER to 1
MultiMedia card:
µC/FS can support MultiMedia & SD cards. You can enable the driver by setting FS_USE_MMC_DRIVER to 1. In order to use it, you will have to provide low-level I/O functions for your card reader hardware. Please take a look at the chapter “MultiMedia & SD card device driver” for details.
CompactFlash card & IDE:FS_USE_IDE_DRIVER to 1
2:fs_port.h【一般是與CPU相關的數據類型】
Usually this file only requires minor modifications, if you are using a very specific CPU. Please also check the type declarations in this file to ensure that they fit with your target processor and compiler.
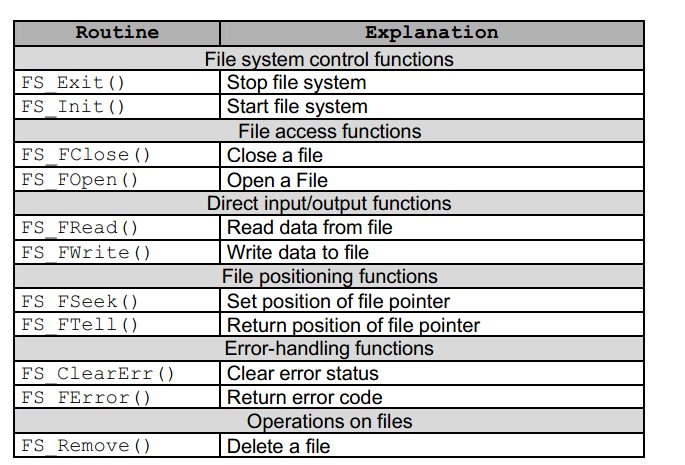
6: API函數說明
FS_IoCtl:執行命令(SD卡等可以通過電腦格式化)
x = FS_IoCtl("ram:",FS_CMD_FORMAT_MEDIA,FS_MEDIA_RAM_16KB,0);
Directory functions
int FS_CloseDir(FS_DIR *dirp);
int FS_MkDir(const char *dirname);
FS_DIR *FS_OpenDir(const char *dirname);
struct FS_DIRENT *FS_ReadDir(FS_DIR *dirp);
void FS_RewindDir(FS_DIR *dirp);
int FS_RmDir(const char *dirname);
7: 設備驅動Device drivers
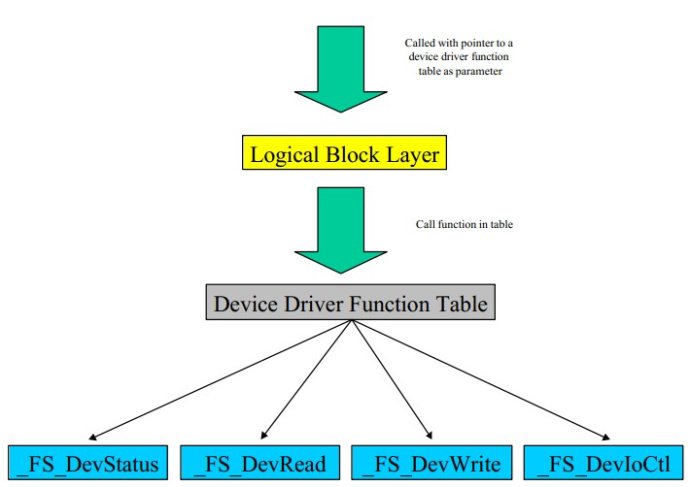
µC/FS可以與任何種類的硬件配合工作;µC/FS需要配備與硬件設備對應的設備驅動程序,這些設備驅動程序包含 基本的訪問硬件的I/O函數 以及 一張全局表,這張表中存放各個函數的指針。【聯想到LINUX中系統調用的系統調用號】
要使你的µC/FS支持特定的硬件設備,你必須寫好該設備的驅動,本節告訴你需要實現哪些函數以及怎么樣將驅動整合到µC/FS中去。
【下面是ramdisk的設備驅動函數表的例子:設備驅動函數表中的各個函數,在PDF中已給出具體的代碼,其他的設備,如MMC&SD也是類似的,需要提供這相關的幾個函數,名字可以不同,在功能函數的次序要一樣】
In this chapter, you will find a detailed description of the device driver functions required by µC/FS. Please note that the names used for these functions are not really relevant for µC/FS because the file system accesses those functions through a function table.
因為是通過一張全局表來管理各個設備驅動函數,所以各設備驅動函數的名稱與µC/FS沒有太多的關聯性。
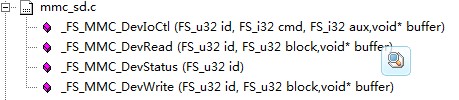
_FS_DevIoCtl():Execute special command on device.
static int _FS_DevIoCtl(FS_u32 id, FS_i32 cmd, FS_i32 aux,void *buffer);
Parameter Meaning
id Number of media (0…N)
cmd Command
aux Parameter for command
buffer Pointer to data required by command
該函數被用來完成一些設備驅動中特殊的命令,對uc/FS來說目前需要支持的這類特殊命令有:FS_CMD_FLUSH_CACHE,這個命令用來告訴設備的緩沖邏輯 所有的緩沖必須清零,如果你的設備沒有緩沖邏輯,該函數不需要做任何事情。
_FS_DevRead():Read block from media
static int _FS_DevRead(FS_u32 id, FS_u32 block, void *buffer);
id Number of media (0…N)
block Block number to be read from the media
buffer Data buffer to which the data is transferred
The function should transfer 0x0200 (i.e. 512) bytes, which is the default value for an MS-DOS/MS-Windows compatible FAT file systems. µC/FS can support any block size but, if you use the FAT file system layer, you have to use this default block size.
函數應該傳送0x0200(512)個字節,這個是兼容FAT文件系統的MS-DOS/MS-Windows系統的默認值,µC/FS能支持任何大小的塊,但是如果你的文件系統層使用FAT,那么你必須使用這個默認的塊大小。
_FS_DevStatus():Return current status of your device.
static int _FS_DevStatus(FS_u32 id); id Number of media (0…N)
The main purpose of this function is to detect a media change. All µC/FS file operation calls this function to check, if the device can be accessed.
該函數的主要目的是檢測一個介質的改變。如果一個設備能夠被訪問,所有的µC/FS 文件操作都調用這個函數進行檢測,
The function returns 0 if the device can be accessed. If the media has changed (e.g. a card removed or replaced) and the device can be accessed, the return value has to be FS_LBL_MEDIACHANGED. Any value < 0 is interpreted as an error.
_FS_DevWrite():Write block to media
static int _FS_DevWrite(FS_u32 id, FS_u32 block,void *buffer);
id Number of media (0…N)
block Block number to be written on media
buffer Pointer to data for transfer to the media.
The function should transfer 0x0200 (i.e. 512) bytes, which is the default value for an MS-DOS/MS-Windows compatible FAT file systems. µC/FS can support any block size but, if you use the FAT file system layer, you have to use this default block size.
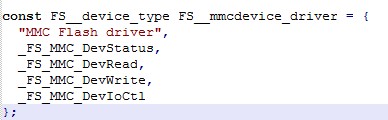
Device driver function table
To use a device driver with µC/FS, a global function table is required, which
holds pointers to the device driver functions. Each entry in the table contains
five values as shown in the example below.
const FS__device_type FS__ramdevice_driver = {
"RAMDISK device",
_FS_DevStatus,
_FS_DevRead,
_FS_DevWrite,
_FS_DevIoCtl
};
If you want to use your own device driver, you have to tell µC/FS, which device
name you would like to use for your device and which File System Layer
(currently only FAT is supported) you want to use.
You do this by setting appropriate value for FS_DEVINFO in your FS_conf.h ,
which is used to initialize µC/FS’s global device information table.
如果你想要使用自己的設備驅動,你必須要告訴μC/FS,你的設備使用的是哪一個設備名稱以及使用哪一個文件系統來管理(目前只支持FAT)。
可以將 FS_conf.h中的FS_DEVINFO 設置一個合適的值來完成上面的動作,FS_DEVINFO被用來初始化μC/FS的全局設備信息表。
【上面是ramdisk的設備驅動函數表的例子,_FS_DevStatus, _FS_DevRead, _FS_DevWrite,
_FS_DevIoCtl,就是ramdisk所需的底層驅動函數】
這里如果是MMC&SD存儲設備,下面是源碼。
#if FS_USE_SMC_DRIVER
#define FS_DEVINFO_DEVSMC
{"smc",&FS__fat_functable,&FS__smcdevice_driver,FS_CACHEINFO_SMC_DRIVER 0 },
#else
#define FS_DEVINFO_DEVSMC
#endif
#if FS_USE_MMC_DRIVER
#define FS_DEVINFO_DEVMMC
{"mmc", &FS__fat_functable,&FS__mmcdevice_driver, FS_CACHEINFO_MMC_DRIVER 0 },
#else
#define FS_DEVINFO_DEVMMC
#endif
......
#endif
從源碼中可以看出,如果沒有定義
FS_DEVINFO宏,且如果沒有定義
FS_DEVINFO_DEVSMC,系統會自動以FS_DEVINFO_DEVSMC,即采用系統默認的設備驅動。
我們可以在fs_conf.h中配置
FS_USE_MMC_DRIVER = 1;再定義
#define FS_DEVINFO \
"mmc", &FS__fat_functable, &FS__mmcdevice_driver, 0,
FS_USE_MMC_DRIVER = 1,即使沒有定義
FS_DEVINFO,系統也會有一個默認的定義。
FS__fat_functable:這個表不用填充,因為這里面的函數在API層已經實現,且系統已經設置好。用戶只需更改FS__mmcdevice_driver里面的各個函數即可。
【這里支持多個設備"smc"和"mydev"】
#define FS_DEVINFO \
"smc", &FS__fat_functable, &FS__smcdevice_driver, 0, \
"mydev", &FS__fat_functable, &FS__mydevice_driver , 0
【如果不指定,系統將使用默認值】
The first parameter is a device name, which you want to use for µC/FS’s API
calls.
The second parameter is a pointer to a File System Layer function table;
currently only FAT is supported.
The third parameter is a pointer to a Device Driver function table.
The last parameter is reserved for future use and should be zero.
8: 各目錄介紹
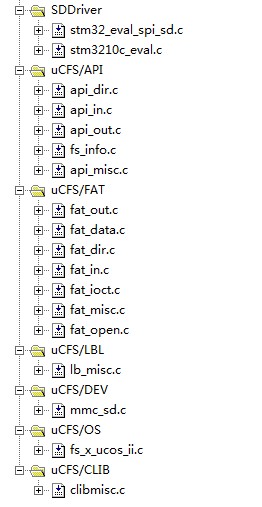
在工程中添加上面的文件組:API層、FAT層、LBL層、DEV層、OS、CLIB
DEV包含的就是文件系統需要使用的最底層的操作硬件的接口,
這里使用文件系統標準的操作接口:_FS_XXX_Devxxx(....):在這幾個函數中調用具體的SD卡的操作函數來實現與硬件驅動的鏈接。
CLIB中包含的是文件系統使用的一些C標準函數。
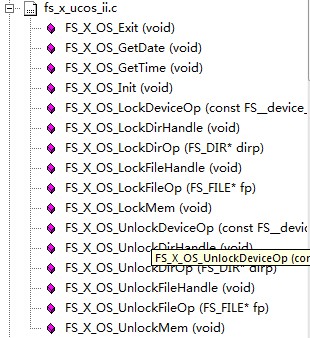
OS組中包含的文件fs_x_ucos_ii.c中包含的就是一些函數接口,這些接口是連接操作系統的接口(當然在裸機下也是這些接口),如果使用操作系統,這些函數接口中 就是與操作系統相關的代碼,如果沒有操作系統,這些接口就是很簡單的一些與系統無關的代碼,總之是文件系統是需要這些接口(有無操作系統接口是一樣的);
各接口函數如下:
FS_X_OS_Init:創建一些文件系統運行時需要使用的一些信號量(用來訪問資源)
FS_X_OS_Exit:刪除上面創建的各信號量
其他的都是配對的Lock/Unlock,也就是申請獲取一個對應的信號量,使用后再釋放這個信號量。
就是這么簡單。
9: MultiMedia & SD card device driver
µC/FS includes a generic driver for MultiMedia & SD cards. The driver accesses
cards using SPI mode.
µC/FS包含一個針對MMC/SD卡的通用驅動,該驅動通過SPI模式訪問卡。
To use the driver in your system, you will have to provide basic I/O functions for
accessing your card reader hardware. You can find samples of these routines in
the directory device\mmc_sd\hardware.
在你的系統中使用該驅動時,你必須要提供基本的能訪問你的讀卡器硬件的I/O函數。你可以在“device\mmc_sd\hardware”路徑下找到例子。
【在源代碼的目錄中官方提供了相關設備的通用底層驅動的例程】
[下面藍色的就是官方提供的MMC&SD卡的通用驅動,但是需要你提供基本的IO訪問函數]
[在device\xxx\hardware目錄下,存放的就是對應的xxx設備的通用驅動, 如smc_X_hw.c、smc_X_hw.h]
FS_MMC_HW_X_BusyLedOff():Turns off busy LED of the card reade
void FS_MMC_HW_X_BusyLedOff(FS_u32 id);
id:ID of card reader (0…N).
FS_MMC_HW_X_BusyLedOn():Turns on busy LED of the card reader.
void FS_MMC_HW_X_BusyLedOn (FS_u32 id);
id:ID of card reader (0…N).
FS_MMC_HW_X_ClockCard()
FS_MMC_HW_X_SetCS()
FS_MMC_HW_X_AdjustFOP()
FS_MMC_HW_X_CheckOCR()
FS_MMC_HW_X_GetFOP()
FS_MMC_HW_X_CheckWP()
FS_MMC_HW_X_DetectStatus()
FS_MMC_HW_X_WaitBusy()
FS_MMC_HW_X_ReadByte()
FS_MMC_HW_X_ReadByteNoSync()
FS_MMC_HW_X_ReadSingleBlock()
FS_MMC_HW_X_WriteByte()
FS_MMC_HW_X_WriteByteSingleBlock()