|
|
|
--用3個單片機引腳讀取10個開關狀態
作者注:此方法并非擴展輸入腳最佳方法,如果需要大量擴展輸入腳的話(幾十甚至上百路),可以使用74HC165或者CD4021做shiftin。而不是本文的4017。
http://playground.arduino.cc/Code/ShiftRegSN74HC165N
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/ShiftIn
The SN74HC165N is an 8-bit parallel-load or serial-in shift registers with complementary serial outputs available from the last stage. When the parallel load (PL) input is LOW, parallel data from the D0 to D7 inputs are loaded into the register asynchronously. When PL is HIGH, data enters the register serially at the Ds input and shifts one place to the right (Q0 → Q1 → Q2, etc.) with each positive-going clock transition. This feature allows parallel-to-serial converter expansion by tying the Q7 output to the DS input of the succeeding stage.
Breadboard SchematicThe following image shows 10 pushbuttons wired to two SN74HC165N input shift registers. Note that the 6 unused input pins are grounded.
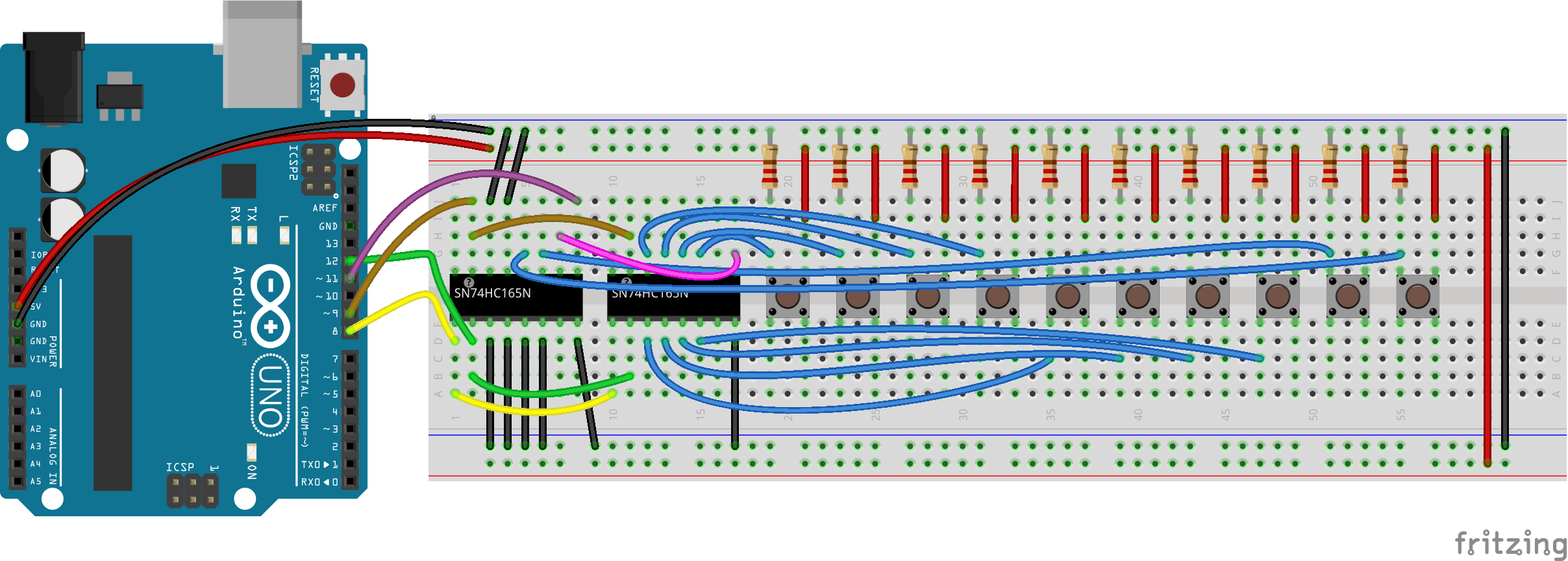
CodeThe following code demonstrates reading in 16 digital states from a pair of daisy-chained SN74HC165N shift registers while using only 4 digital pins on the Arduino.
- /*
- * SN74HC165N_shift_reg
- *
- * Program to shift in the bit values from a SN74HC165N 8-bit
- * parallel-in/serial-out shift register.
- *
- * This sketch demonstrates reading in 16 digital states from a
- * pair of daisy-chained SN74HC165N shift registers while using
- * only 4 digital pins on the Arduino.
- *
- * You can daisy-chain these chips by connecting the serial-out
- * (Q7 pin) on one shift register to the serial-in (Ds pin) of
- * the other.
- *
- * Of course you can daisy chain as many as you like while still
- * using only 4 Arduino pins (though you would have to process
- * them 4 at a time into separate unsigned long variables).
- *
- */
- /* How many shift register chips are daisy-chained.
- */
- #define NUMBER_OF_SHIFT_CHIPS 2
- /* Width of data (how many ext lines).
- */
- #define DATA_WIDTH NUMBER_OF_SHIFT_CHIPS * 8
- /* Width of pulse to trigger the shift register to read and latch.
- */
- #define PULSE_WIDTH_USEC 5
- /* Optional delay between shift register reads.
- */
- #define POLL_DELAY_MSEC 1
- /* You will need to change the "int" to "long" If the
- * NUMBER_OF_SHIFT_CHIPS is higher than 2.
- */
- #define BYTES_VAL_T unsigned int
- int ploadPin = 8; // Connects to Parallel load pin the 165
- int clockEnablePin = 9; // Connects to Clock Enable pin the 165
- int dataPin = 11; // Connects to the Q7 pin the 165
- int clockPin = 12; // Connects to the Clock pin the 165
- BYTES_VAL_T pinValues;
- BYTES_VAL_T oldPinValues;
- /* This function is essentially a "shift-in" routine reading the
- * serial Data from the shift register chips and representing
- * the state of those pins in an unsigned integer (or long).
- */
- BYTES_VAL_T read_shift_regs()
- {
- long bitVal;
- BYTES_VAL_T bytesVal = 0;
- /* Trigger a parallel Load to latch the state of the data lines,
- */
- digitalWrite(clockEnablePin, HIGH);
- digitalWrite(ploadPin, LOW);
- delayMicroseconds(PULSE_WIDTH_USEC);
- digitalWrite(ploadPin, HIGH);
- digitalWrite(clockEnablePin, LOW);
- /* Loop to read each bit value from the serial out line
- * of the SN74HC165N.
- */
- for(int i = 0; i < DATA_WIDTH; i++)
- {
- bitVal = digitalRead(dataPin);
- /* Set the corresponding bit in bytesVal.
- */
- bytesVal |= (bitVal << ((DATA_WIDTH-1) - i));
- /* Pulse the Clock (rising edge shifts the next bit).
- */
- digitalWrite(clockPin, HIGH);
- delayMicroseconds(PULSE_WIDTH_USEC);
- digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
- }
- return(bytesVal);
- }
- /* Dump the list of zones along with their current status.
- */
- void display_pin_values()
- {
- Serial.print("Pin States:");
- for(int i = 0; i < DATA_WIDTH; i++)
- {
- Serial.print(" Pin-");
- Serial.print(i);
- Serial.print(": ");
- if((pinValues >> i) & 1)
- Serial.print("HIGH");
- else
- Serial.print("LOW");
- Serial.print("");
- }
- Serial.print("");
- }
- void setup()
- {
- Serial.begin(9600);
- /* Initialize our digital pins...
- */
- pinMode(ploadPin, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(clockEnablePin, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(clockPin, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(dataPin, INPUT);
- digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
- digitalWrite(ploadPin, HIGH);
- /* Read in and display the pin states at startup.
- */
- pinValues = read_shift_regs();
- display_pin_values();
- oldPinValues = pinValues;
- }
- void loop()
- {
- /* Read the state of all zones.
- */
- pinValues = read_shift_regs();
- /* If there was a chage in state, display which ones changed.
- */
- if(pinValues != oldPinValues)
- {
- Serial.print("*Pin value change detected*");
- display_pin_values();
- oldPinValues = pinValues;
- }
- delay(POLL_DELAY_MSEC);
- }
使用Arduino做制作,需要有一組開關控制Arduino狀態。但是Arduino引腳不多,傳統接法開關多了要占用很多引腳。減少引腳的方法有很多,可以選矩陣方式,編碼器方式,還有本文要介紹的分時復用開關法等。
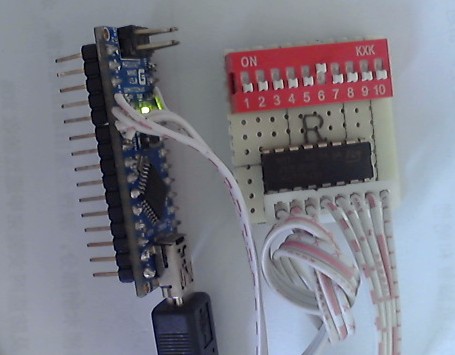
特點:十個開關占用三個數據引腳,之后每增加十個開關就增加一個引腳。
4017是一塊十進制計數器,每輸入一個CLK脈沖,Q0~Q9輪流產生高電平。每時刻有且只有一個引腳高電平。
二極管防止多個開關閉合時,有的輸出端輸出高電平,有的輸出低電平,互相接上的話,會低電平引腳會干擾高電平腳的工作。
開關用10路撥動式小型開關,或者自己選擇其他開關形式。
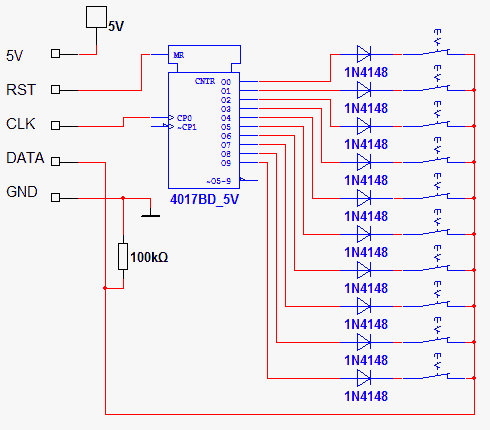
電路工作原理:
- 先在RST(4017的復位腳MR)發出一個脈沖,使4017復位。
- 此時有且只有Q0輸出高電平(Q0對應開關S1,Q9對應開關S10),讀取一次輸出信號DATA。如果第一個開關S1閉合了,應該DATA得到高電平;如果S1斷開了,就DATA得到低電平。此時記DATA結果對應第一個開關S1的狀態。
- 給CLK輸出一個脈沖,讓4017移位,有且只有Q1輸出高電平(Q0,Q2~Q9均為低電平)。讀取DATA。得到S2狀態。
- 不斷給CLK脈沖。總共給10次脈沖,讓4017由Q0移動到Q9,完成一次開關遍歷,每次移動獲取一次DATA狀態。存為S1~S10狀態。
電路原理圖如圖:
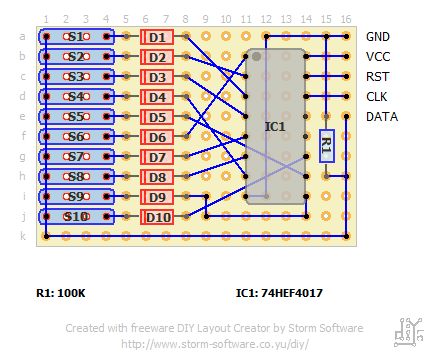
洞洞板圖(由于引腳多,不建議面包板制作。)
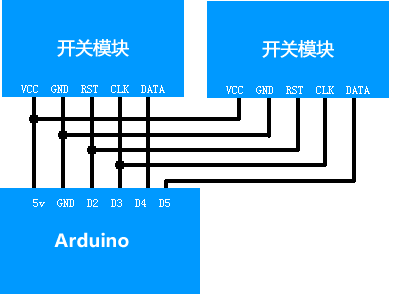
關于在一塊Arduino上使用多塊模塊:每增加一塊模塊,可以增加十路開關(當然你也可以使用兩塊4017做成行列矩陣控制100個開關。不過那個就屬于另外話題了)。增加的方式是將兩塊模塊的RST,CLK,VCC,GND接在一起,接到單片機的相應引腳,然后兩個模塊的DATA腳分別接單片機兩個IO口。
Arduino程序例子:
const int rst = 2; //板子的RST腳接Arduino的D4口(自定義)
const int clk = 3; //板子的CLK腳接Arduino的D3口(自定義)
const int data1 = 4; //板子的DATA腳接Arduino的D2口(自定義)
//const int data2 = 5; //如果有第二塊板子的話,兩塊板子共用RST和CLK引腳。DATA接Arduino的D5口,第三塊板子可以類推接D6口(自定義)
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(rst, OUTPUT);
pinMode(clk, OUTPUT);
pinMode(data1, INPUT);
//pinMode(data2,INPUT); //如果有第二塊板子的話要定義IO
}
void loop()
{
int KeyStatus[10] = {0}; //按照總開關數定義。可能要改為20,30等
digitalWrite(rst, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10); //所有delayMicroseconds(10);均是給4017一個反應時間。
digitalWrite(rst, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(10);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
KeyStatus = digitalRead(data1);
//KeyStatus[i+10] = digitalRead(data2); //讀取第二個板子的狀態,地址放在i+10
digitalWrite(clk, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(clk, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(10);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) //循環打印KeyStatus數組,i<10可能要改為i<20,30等
{
Serial.print(KeyStatus);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
delay(100);
}
洞洞板實物圖:


|
|